Login or create an account
CloseReturning Customer
I am a returning customer
Login or create an account
CloseRegister Account
If you already have an account with us, please login at the login form.
Your Account Has Been Created!
Thank you for registering with Welcome to Supertechnical!
You will be notified by e-mail once your account has been activated by the store owner.
If you have ANY questions about the operation of this online shop, please contact the store owner.
Account Logout
You have been logged off your account. It is now safe to leave the computer.
Your shopping cart has been saved, the items inside it will be restored whenever you log back into your account.
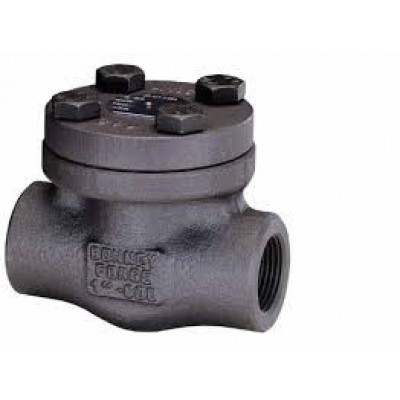
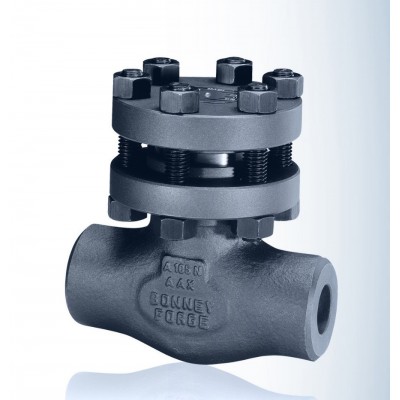
Check Valve
Check Valves
Bonney Forge valves
are available in two bonnet designs. The first design is the Bolted Bonnet,
with male-female joint, spiral wound gasket, made in F316L/graphite. Ring joint
gasket are also available on request. The second design is the welded bonnet,
with a threaded and seal welded joint. On request a full penetration strength
welded joint is available.
The check valves are
also available in three different design configurations. These are piston
check, ball check, or swing check designs
Swing Type
The disk swings away from the valve-seat to allow flow in the
forward direction, and returns to the valve-seat when upstream flow is stopped,
to prevent backflow. Swing check design is one of the most common and best
check valve for general-purpose use. These valves produce the lowest pressure
drop, when compared with other check valves of the same size, the internal
contours and shapes allow them to fully open at low fluid velocities and create
a smooth flow path through the valve. The design is simple and easy to maintain
and can be used for either horizontal or vertical (fluid flowing upward) pipe
layouts. Because of their design, swing checks are not fast-closing valves due
to the travel distance from full open to close.
Piston Type
The pressure of the fluid passing through a system opens the
valve, while any reversal of flow will close the valve. In Piston, or lift,
check valves a body-guided disc moves within the body bore. The body guide
ensures alignment of the seat and disc when the valve closes. The valve is
installed with the flow under the disc, so that the inlet line pressure and
flow rate will force the disc to “lift” off the seat and allow the line fluid
to flow through the valve. Should the flow suddenly reverse itself, the disc
will automatically and quickly, assisted by the weight of the disc, be forced
to the closed position, preventing the line fluid from returning. Exercise
caution when these valves are used for dirty media because that media could
cause the disc to stick inside the body bore.
BALL Check valve
The function of ball check valves is similar to the piston check, but the ball
check valves use a “ball” inside the body to control the movement of flow. The ball is free to rotate, resulting in even
wear and a wiping action between the ball and seat. This feature makes ball
checks useful for viscous media.
Product Range
·
Size - From NPS 1/2 TO NPS 3
·
Class - 150 to ASME 4500
Applicable Standards
·
Design -
API 602 - ISO 15761 - ASME
B16.34
·
Inspection & testing - API 598
·
Marking - MSS
SP-25
·
Rating - ASME
B16.34
·
Fugitive emission - NA
End connection
·
Face to face - ASME B16.10
·
End to end - Manufacturer standard or ASME B16.10
·
Socket weld - ASME B16.11
·
Screwed ends(NPT) - ASME B1.20.1
·
Flanged ends - ASME B16.5
·
Butt welding ends - ASME B16.25
Check Valves
Bonney Forge valves
are available in two bonnet designs. The first design is the Bolted Bonnet,
with male-female joint, spiral wound gasket, made in F316L/graphite. Ring joint
gasket are also available on request. The second design is the welded bonnet,
with a threaded and seal welded joint. On request a full penetration strength
welded joint is available.
The check valves are
also available in three different design configurations. These are piston
check, ball check, or swing check designs
Swing Type
The disk swings away from the valve-seat to allow flow in the
forward direction, and returns to the valve-seat when upstream flow is stopped,
to prevent backflow. Swing check design is one of the most common and best
check valve for general-purpose use. These valves produce the lowest pressure
drop, when compared with other check valves of the same size, the internal
contours and shapes allow them to fully open at low fluid velocities and create
a smooth flow path through the valve. The design is simple and easy to maintain
and can be used for either horizontal or vertical (fluid flowing upward) pipe
layouts. Because of their design, swing checks are not fast-closing valves due
to the travel distance from full open to close.
Piston Type
The pressure of the fluid passing through a system opens the
valve, while any reversal of flow will close the valve. In Piston, or lift,
check valves a body-guided disc moves within the body bore. The body guide
ensures alignment of the seat and disc when the valve closes. The valve is
installed with the flow under the disc, so that the inlet line pressure and
flow rate will force the disc to “lift” off the seat and allow the line fluid
to flow through the valve. Should the flow suddenly reverse itself, the disc
will automatically and quickly, assisted by the weight of the disc, be forced
to the closed position, preventing the line fluid from returning. Exercise
caution when these valves are used for dirty media because that media could
cause the disc to stick inside the body bore.
BALL Check valve
The function of ball check valves is similar to the piston check, but the ball
check valves use a “ball” inside the body to control the movement of flow. The ball is free to rotate, resulting in even
wear and a wiping action between the ball and seat. This feature makes ball
checks useful for viscous media.
Product Range
·
Size - From NPS 1/2 TO NPS 3
·
Class - 150 to ASME 4500
Applicable Standards
·
Design -
API 602 - ISO 15761 - ASME
B16.34
·
Inspection & testing - API 598
·
Marking - MSS
SP-25
·
Rating - ASME
B16.34
·
Fugitive emission - NA
End connection
·
Face to face - ASME B16.10
·
End to end - Manufacturer standard or ASME B16.10
·
Socket weld - ASME B16.11
·
Screwed ends(NPT) - ASME B1.20.1
·
Flanged ends - ASME B16.5
·
Butt welding ends - ASME B16.25




